Aloin (Alo), a major compound found in aloes, has been widely recognized for its pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, hypoglycemic, and antioxidant effects. However, its specific efficacy and molecular mechanisms of action in the treatment of sepsis remain unidentified. Associate Professor Su Jingqian’s research team constructed a mouse model closely resembling the clinical course of sepsis in humans by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) to systematically evaluate the therapeutic effect of Alo and its underlying mechanisms.
The research findings, titled “Aloin ameliorates cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis in mice by attenuating inflammation and modulating gut microbiota,” were published in Food Science and Human Wellness. This study investigated the therapeutic function and mechanisms of action of Alo against sepsis in depth, providing new scientific insights into the nutritional value and pharmacological effects of aloes.
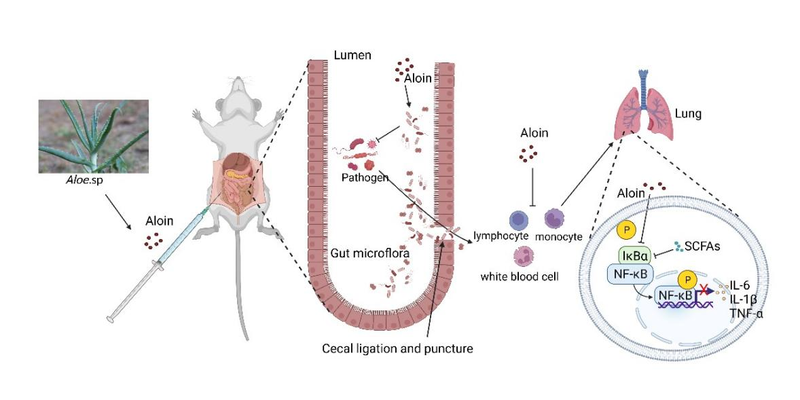
The results showed that Alo displayed a significant therapeutic effect in CLP-induced sepsis in mice. Through the study of the animal model, it was found that Alo significantly improved the survival rate of septic mice, downregulated the expression of proinflammatory factors, and decreased the infiltration of inflammatory cells in tissues and the number of bacteria in the abdominal cavity. Furthermore, Alo altered the composition of the gut microbiome, and particularly promoted the growth of lactobacillus. Further study on the mechanism revealed that Alo effectively suppressed the NF-κB/NLRP3/Caspase signaling, thereby exerting its anti-septic effects.
FNU is the sole institution for completing the research, which was mainly conducted at College of Life Sciences, Biomedical Research Center of South China, and Southern Institute of Oceanography of FNU. Associate Professor Su Jingqian, Xiao Jianbin, a master student from the class of 2019 of FNU, Chen Siyuan, a master student from the class of 2020 of FNU, and Zhao Heng, a doctoral student from the class of 2020 of FNU, are the co-first authors of the paper, and Associate Professor Su Jingqian, Dr. Chen Duo, and Professor Chen Qi are the co-corresponding authors. The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology, the Xiyuanjiang Scholars Program of FNU College of Life Sciences, and so on.
(Translated by Xiao Zhiying/ Reviewed by Xie Xiujuan)
